Collection: Bare Root Grape Vines
Organic Bare Root Grape Vines for Sale
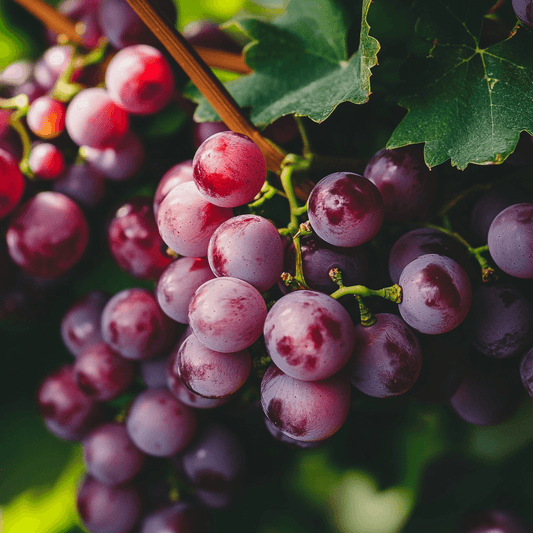
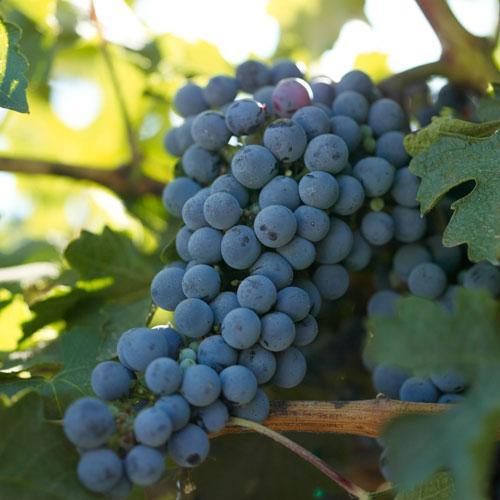
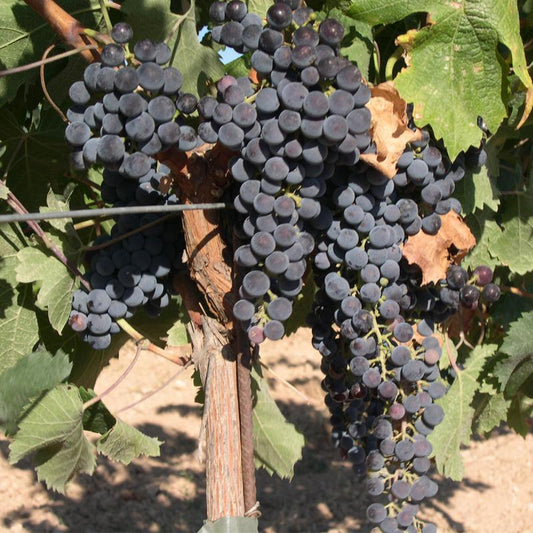
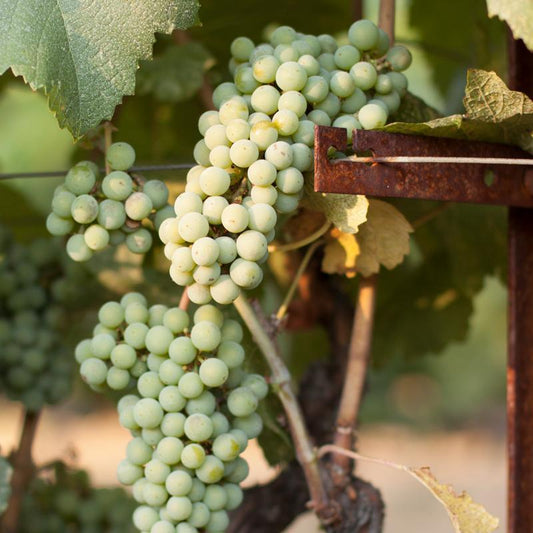
Looking to grow your own grapes? Our bare root grape vines for sale are the perfect starting point for gardeners and vineyard enthusiasts alike. These organic grape vines are grown without synthetic chemicals and are available in a wide variety of options—ideal for both vineyard grapes and backyard gardens.
We offer a curated selection of grape vines in bare root form, including popular bare root grape vines, bare root grapes, and grape vines for sale across hardiness zones 5–11. Whether you're starting a vineyard or simply adding a few vines to your garden, you'll find high-quality plants ready to thrive.
Choosing the Right Grape Plants for Sale
When selecting grape plants for sale, keep these important factors in mind:
-
Available Varieties: Choose from table grapes like Flame Seedless, Black Monukka, Princess, and Reliance—or wine varieties like Cabernet Sauvignon, Zinfandel, Chardonnay, Merlot, and Pinot Noir. We also offer seedless grapes plants for sale for those who prefer grapes without seeds.
-
Sun Requirements: Grape vines thrive in full sun, needing 6–8 hours of direct light per day.
-
Climate Compatibility: Suitable for USDA zones 5 through 11.
How to Plant and Care for Your Grape Vines
To ensure a successful harvest from your grape vines for sale, follow these key tips:
-
Planting: Soak bare root grapes in water for several hours before planting. Plant after the danger of frost has passed.
-
Training & Pruning: Train vines on trellises or arbors. Prune annually to improve airflow, fruit production, and shape.
-
Soil & Water: Use well-draining soil. Water deeply and regularly during the first year to establish healthy roots.
-
Fertilization: Minimal fertilizer is needed for organic grape vines; compost works well.
Harvest & Enjoy Your Grapes
Once your vines mature, enjoy the versatility of your harvest:
-
Fresh Eating: Enjoy table grapes straight from the vine.
-
Winemaking: Use your vineyard grapes like Merlot or Chardonnay for home winemaking.
-
Preserving & Recipes: Make jams, jellies, or add fresh grapes to salads and desserts.
-
Seedless Snacking: Our seedless grapes plants for sale offer sweet, convenient, seed-free fruit.
Why Buy Bare Root Grape Vines from Us
- Wide range of varieties for wine and table use
- All plants sold as bare root grape vines for sale—ideal for spring planting
- Excellent support for home gardeners and small vineyards
- Offers both grape plants for sale and seedless grapes plants for sale with full growing support
Helpful Growing Resources
Get the most out of your grape vines with these expert-written guides, videos, and growing tips:
Articles:
Videos:
Start Your Vineyard or Garden Today
Ready to grow? Browse our full range of bare root grape vines for sale, including seedless grapes plants for sale, and start your grape-growing journey today. Whether you're planting for wine, fresh eating, or creating a beautiful trellised garden, our grape vines will give you years of fruitful harvests.
 Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out
















