Table grape vines are a versatile addition to any garden or landscape. These vines offer succulent and flavorful grapes and serve as ornamental elements, providing summer shade, arbors, or leafy walls. There are two primary classes of table grape vines: European and American. Discover the unique characteristics, uses, and cultivation requirements of our premium grape vines to help you select the perfect variety for your garden. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or just starting out, our high-quality grape vines are the ideal choice for growing delicious grapes right in your backyard.
European Table Grape Vines
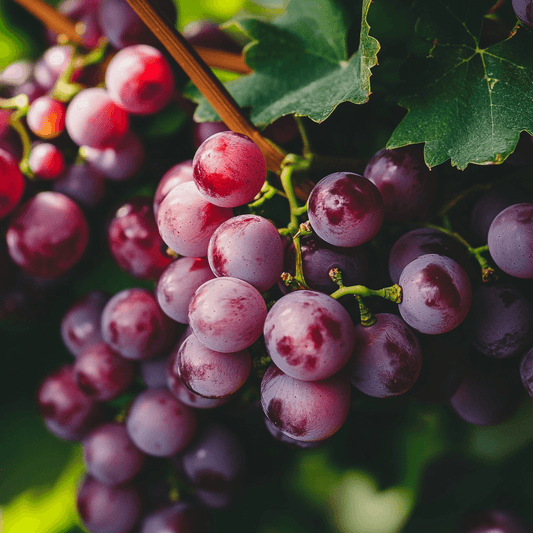
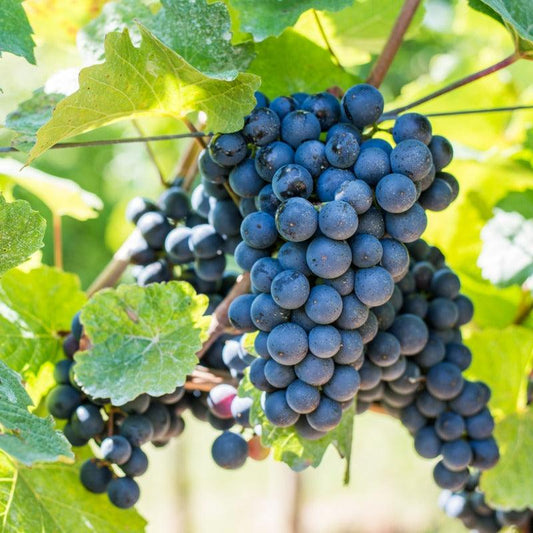
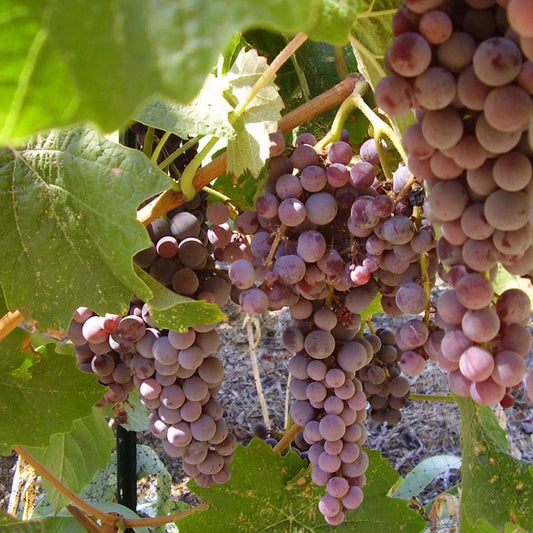
European table grape vines are renowned for their tight skins and wine-like flavors. These grapes typically have high heat requirements for ripening, making them well-suited for regions with warm climates, such as California. European table grapes are the most common grapes grown in California and find diverse applications, including consumption in their fresh form, drying to produce raisins, and for making juices or wine. However, it's important to note that European varieties are susceptible to powdery mildew, a fungal disease. To combat this, regular dusting or spraying with sulfur or other mildew control measures is essential for their health and productivity.
American Table Grape Vines
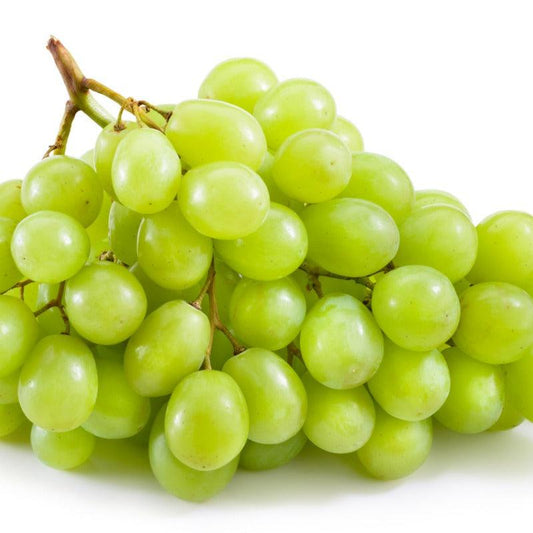
American table grape vines, on the other hand, offer grapes with a flavor reminiscent of Concord grapes. These vines have more moderate heat requirements for ripening and tend to be late bloomers. One notable advantage of American table grape vines is their resistance to powdery mildew, which makes them a low-maintenance choice for grape enthusiasts. Their unique flavor and disease resistance make them popular for home gardeners and commercial growers alike.
Cultivation Requirements
Regardless of whether you opt for European or American table grape vines, there are some common cultivation requirements to consider for successful growth and fruit production. Both classes of vines can thrive in warm sites at lower elevations. However, they share the need for deep, moderately fertile soils that provide the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
Regular pruning is another essential aspect of maintaining table grape vines. Pruning helps control the size of the vine, encourages air circulation, and ensures high-quality grape production. Pruning should be performed during the dormant season to remove old and unproductive wood, promoting new growth.
Self-Fertile Characteristics
Table grape vines have the advantage of being self-fertile. This means that they do not require a second grape vine for pollination; a single vine can produce fruit independently. This makes them a practical choice for gardeners with limited space or those looking for a low-maintenance fruit-bearing plant.
Plant Quality
When acquiring table grape vines, ensuring you are getting quality plants is crucial. Typically, these vines are self-rooted from cuttings and are available as 1-year-old plants. Look for number 1 grade vines with approximately 8 inches of top growth, as these are indicators of healthy and vigorous plants that are more likely to thrive in your garden.
Table grape vines, whether European or American, offer a delightful combination of beauty and utility for your garden. Understanding their distinct characteristics, uses, and cultivation requirements can help you choose the right variety for your specific needs and growing conditions. Whether you dream of enjoying fresh grapes straight from the vine or desire a picturesque arbor covered in lush foliage, table grape vines can make your garden more vibrant and fruitful.
 Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out Sold out
Sold out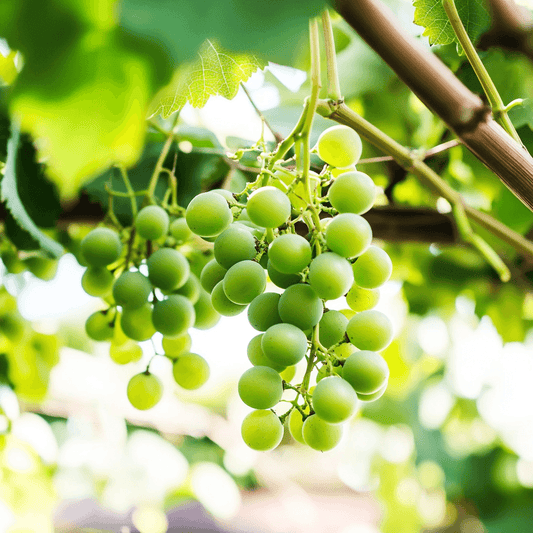 Sold out
Sold out











