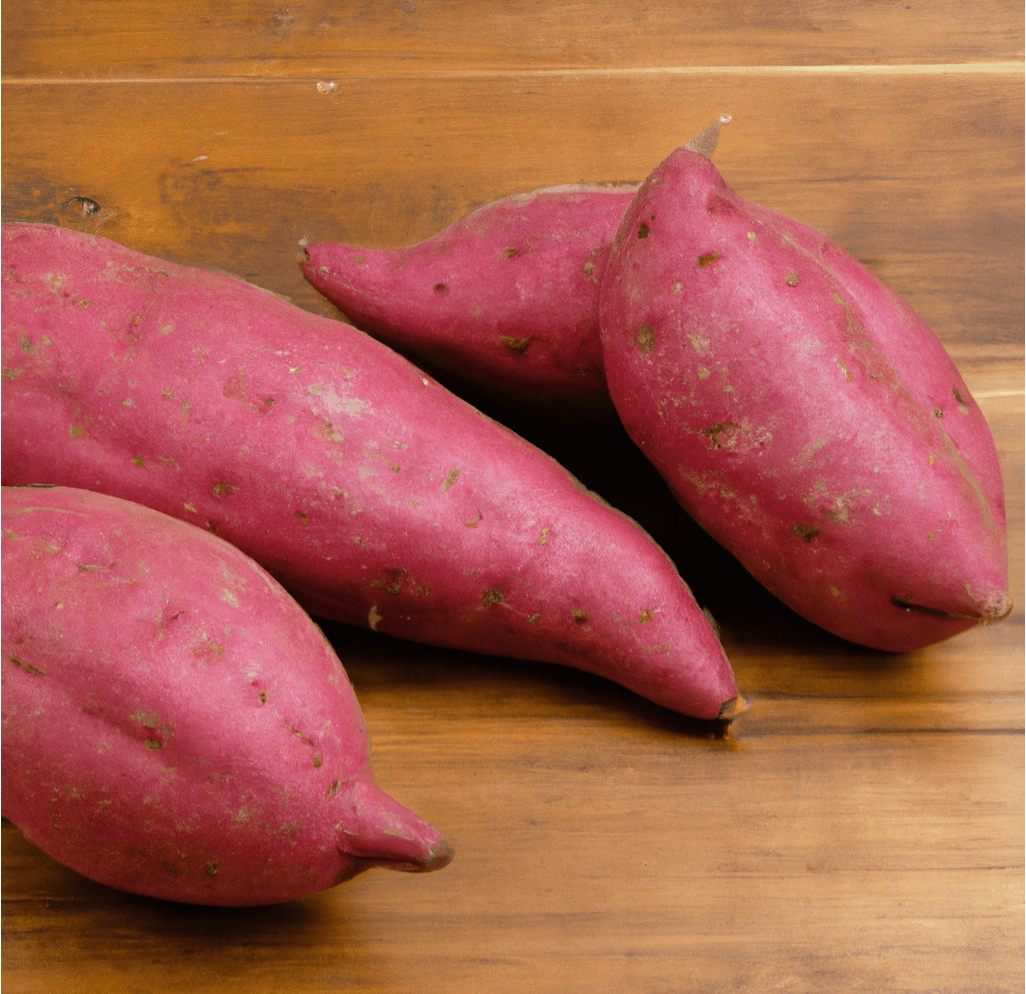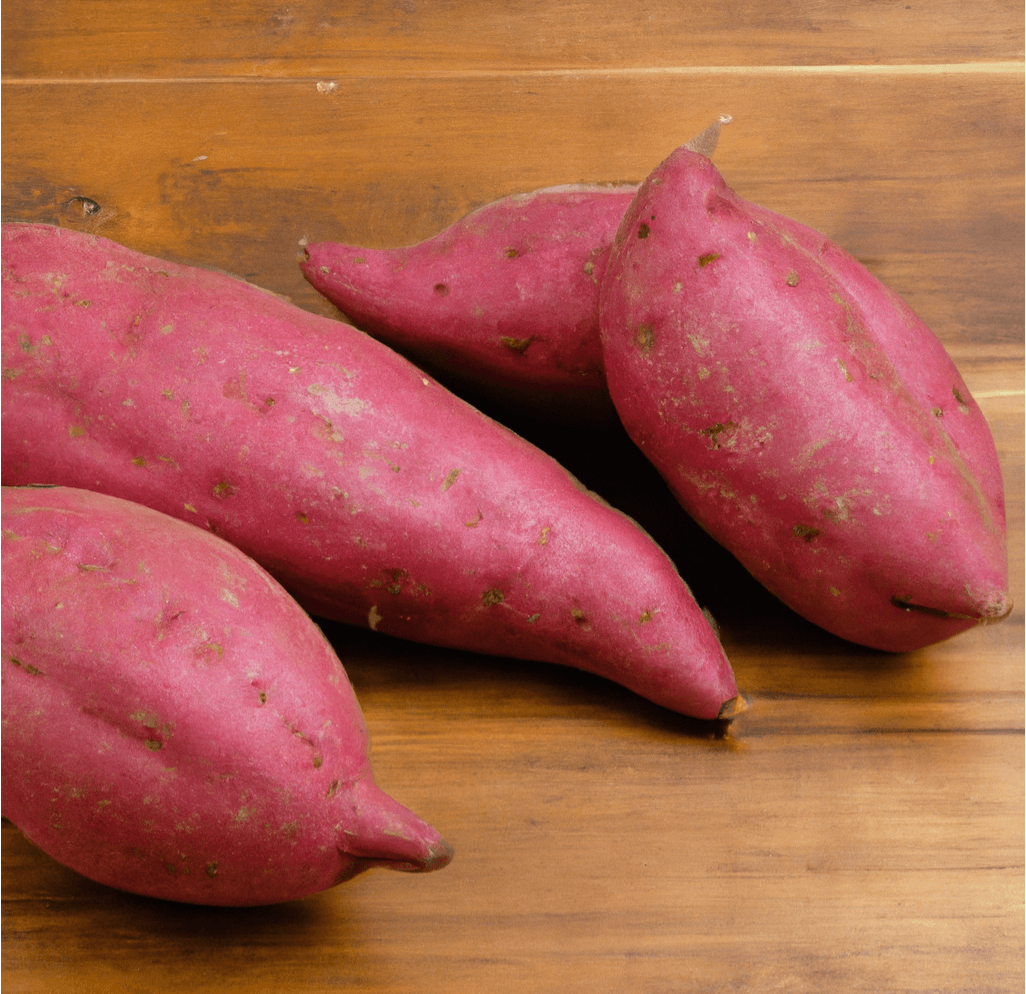Item Number: SP312
Red Japanese Sweet Potato Slips
Vibrant Tastes, Homegrown
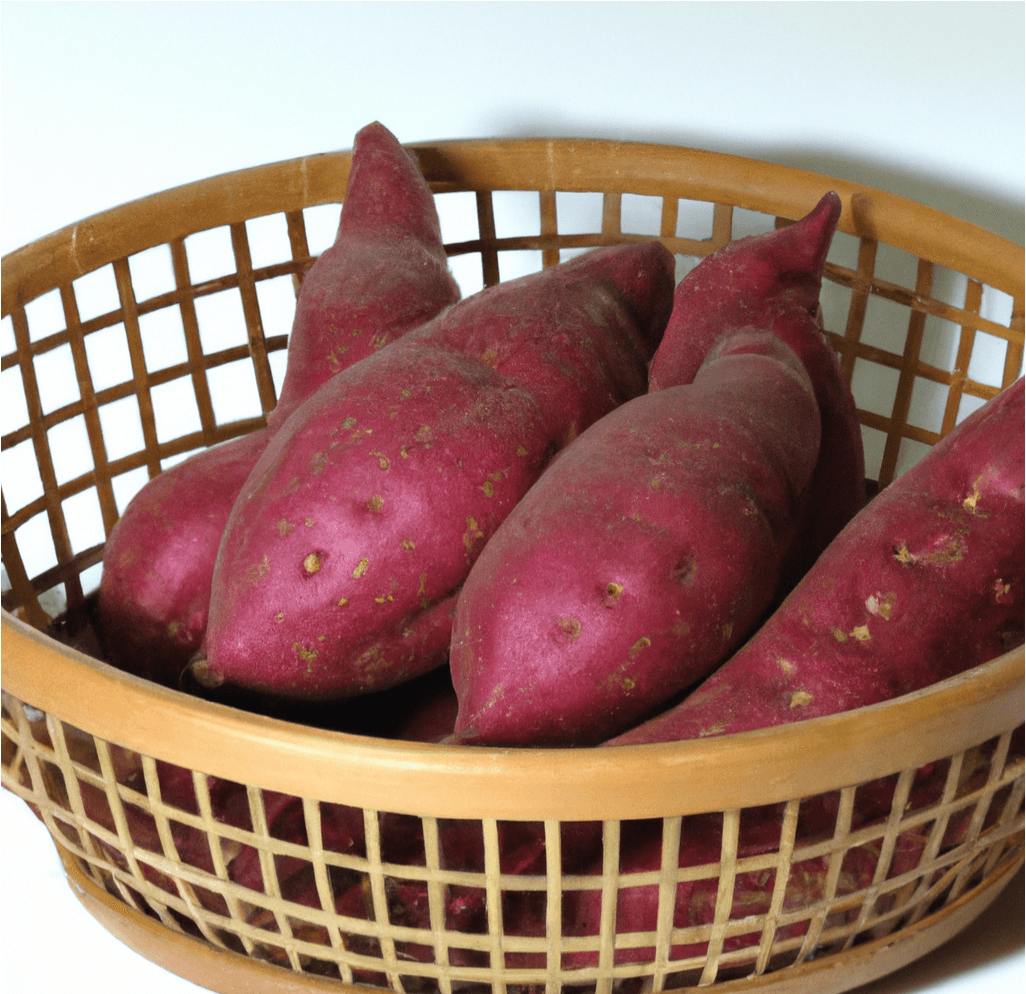
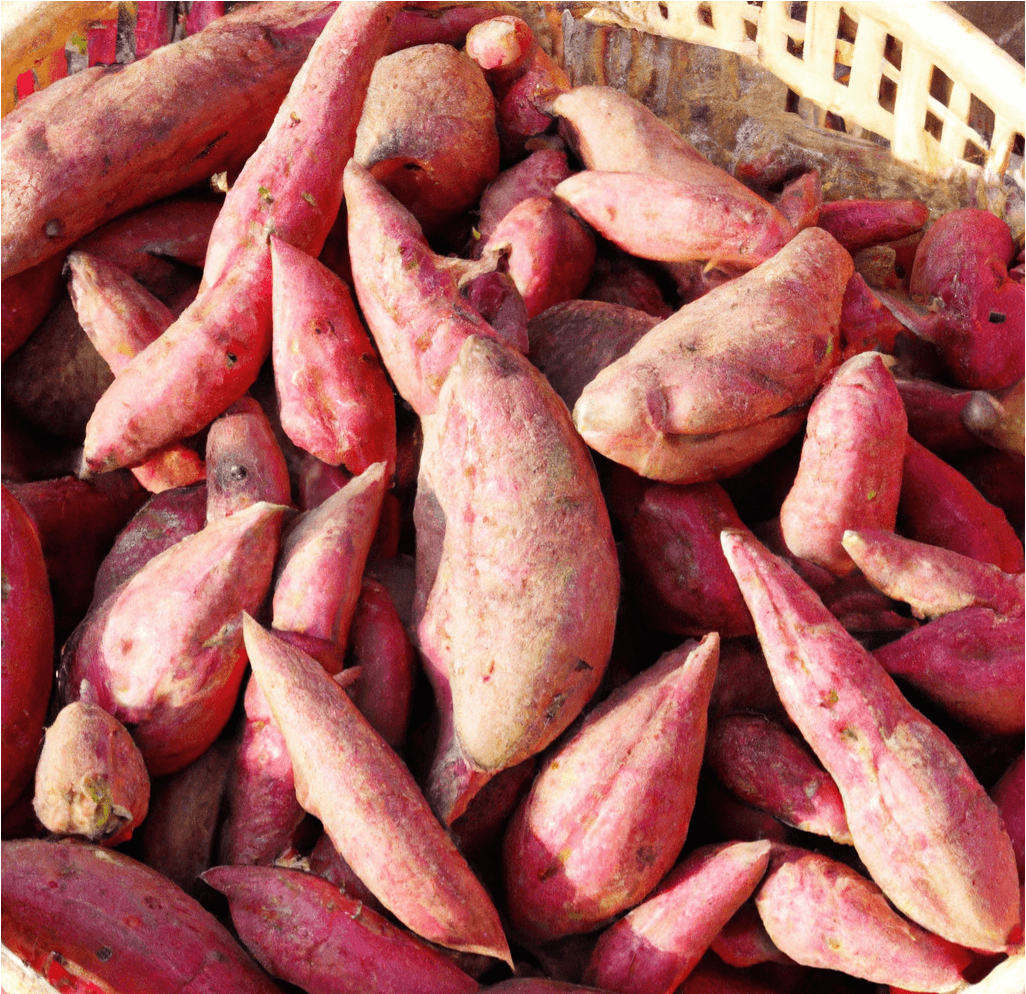
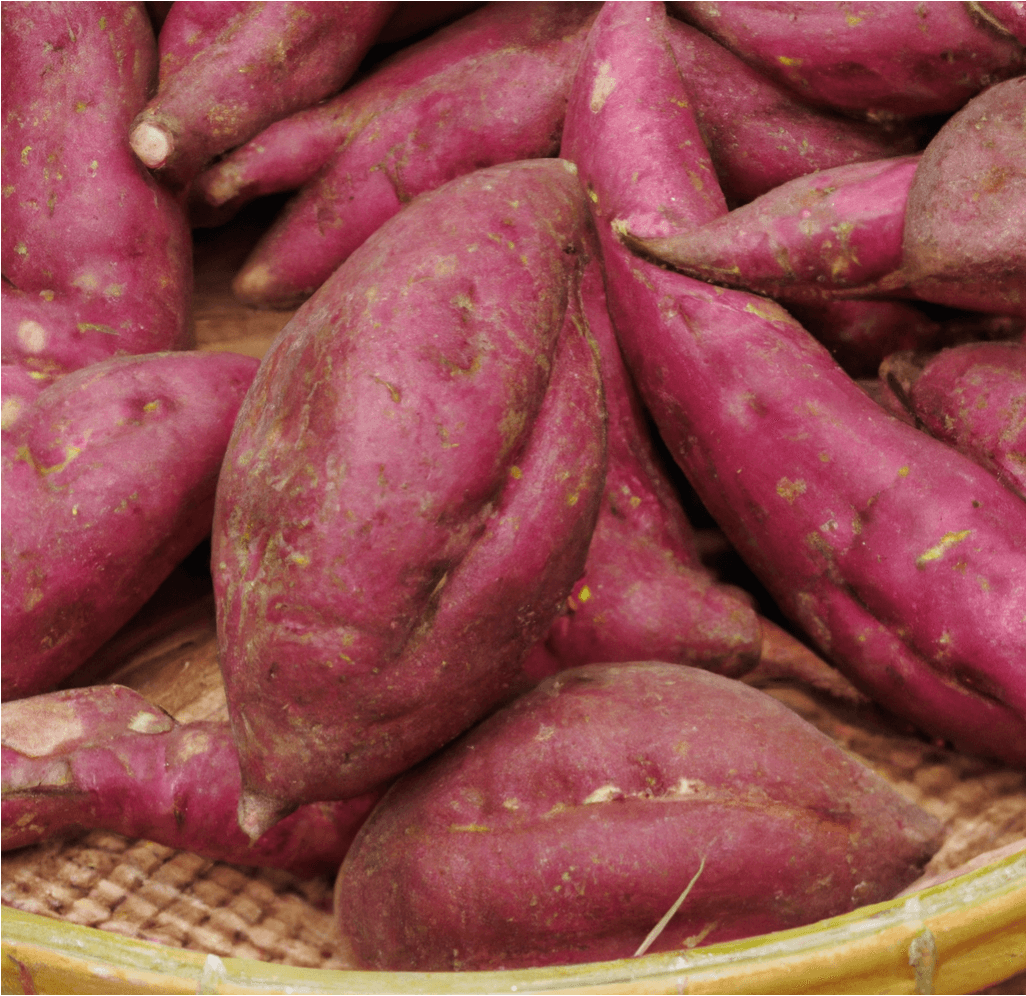
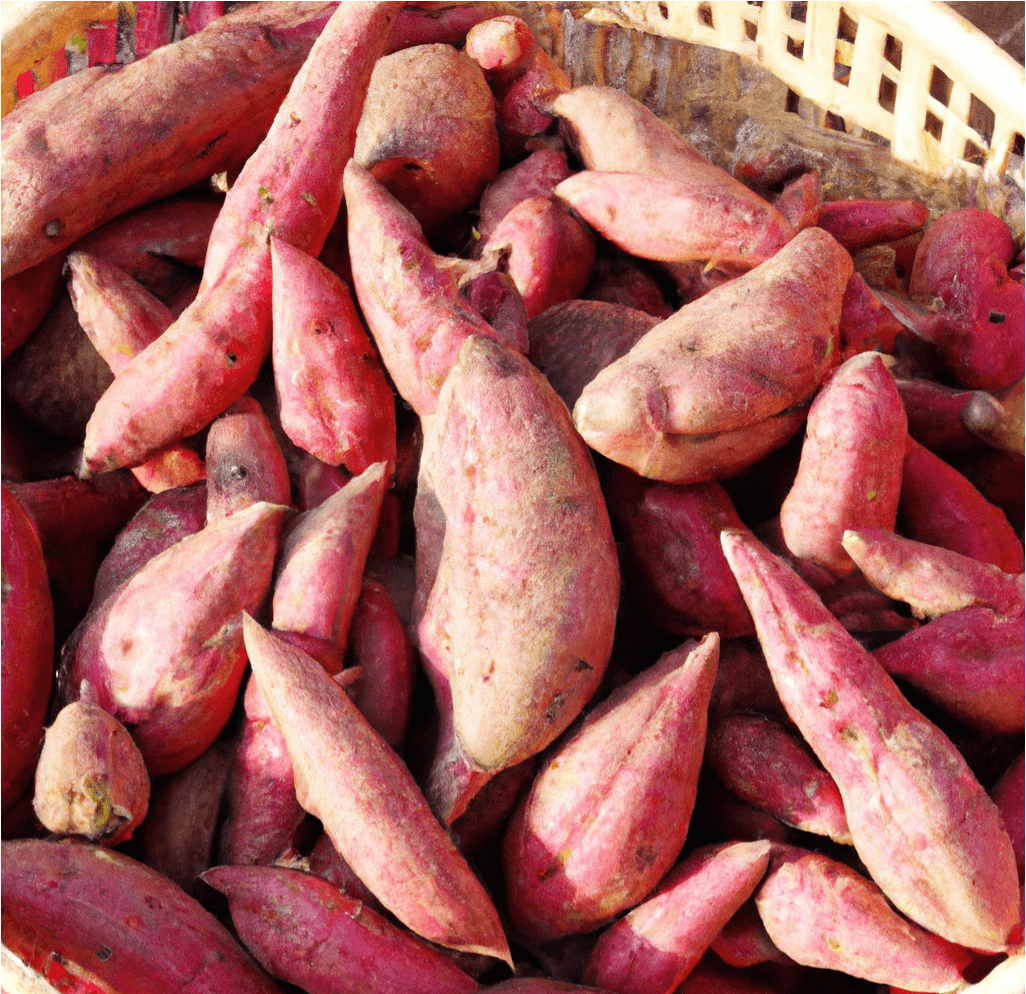
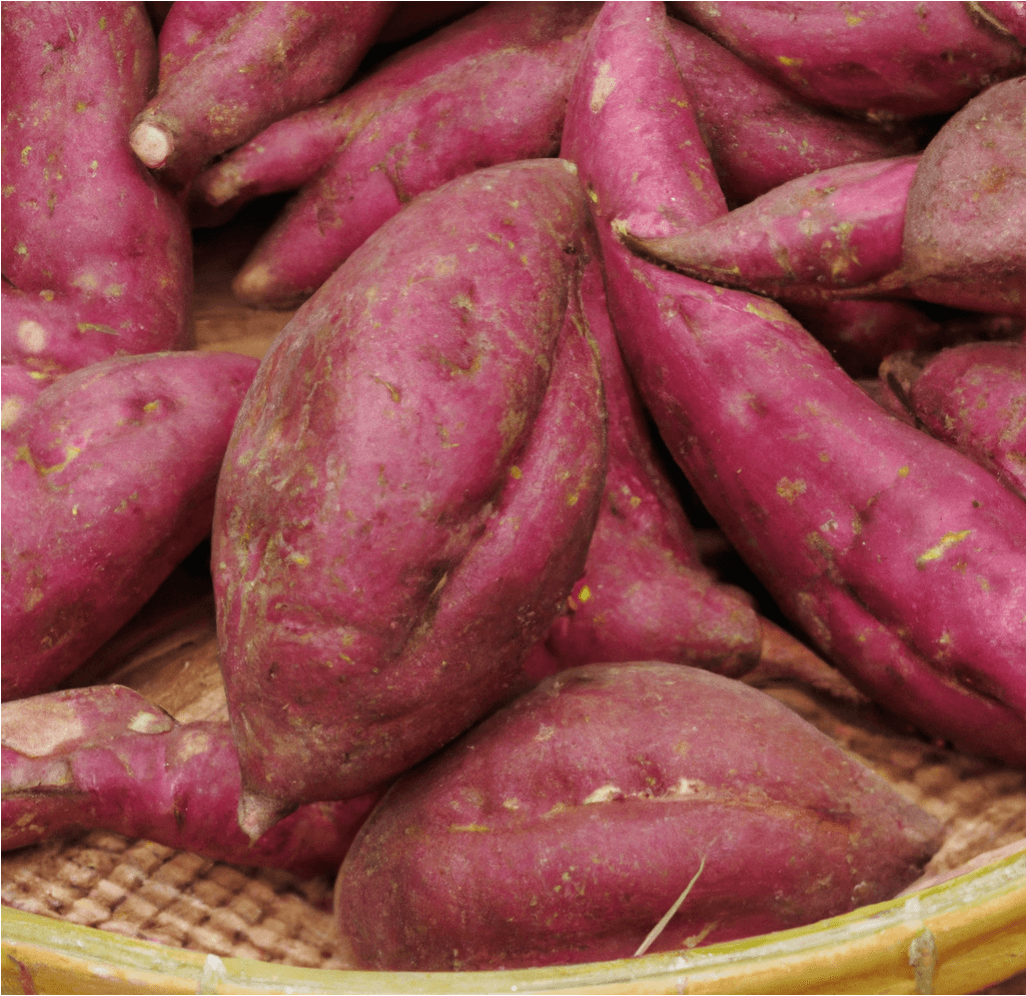
Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes, known for their bright purple skin and white flesh, are a versatile and popular variety. Widely grown in California primarily for Asian food markets, this adaptable variety produces well even without optimal heat and season length. In Japan, this variety is appreciated for its dry flesh, making it ideal for frying, baking into sweets and breads, or simply steaming and minimally seasoning. This guide provides detailed information on how to grow and care for Red Japanese Sweet Potato slips to ensure a successful harvest.
Characteristics of Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Appearance: Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes have a distinctive bright purple skin and creamy white flesh.
- Flavor and Texture: Known for their dry flesh, they are highly valued for their suitability in various culinary applications, including frying, baking, and steaming.
- Maturity: Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes are a short-season variety, typically maturing in 90 to 105 days.
- Climate Adaptability: This variety is adaptable and can be successfully grown in both northern and southern states, making it a versatile option for gardeners across different climates.
Selecting and Preparing the Site:
- Climate: Sweet potatoes thrive in warm climates and require a long growing season with at least 90 to 120 frost-free days. Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes are particularly suited for shorter seasons and can perform well even in cooler climates.
- Soil: Sweet potatoes prefer well-drained, sandy loam soil with a pH between 5.8 and 6.2. The soil should be loose and free of stones or debris to allow the roots to expand easily.
- Sunlight: Choose a location that receives full sun for at least 6 to 8 hours per day. Sweet potatoes need ample sunlight to produce high yields.
Preparing the Slips:
- Fill a tray half way with potting soil or Quickroot and moisten.
- Put your whole sweet potato on top of the soil horizontally and add about an inch of soil but do not completely cover.
- Place the tray on a heating mat, and to speed up the sprouting, place your tray under a grow light.
- Keep the soil moist but not soggy
- In about a week, there should be roots coming from the bottom and small sprouts forming on the top or sides.
- Allow the sprouts to grow to at least 6 inches long.
- This process will take about 4-6 weeks.
Rooting the Slips
- Once the sprouts are at least 6 inches long remove them from the sweet potato by cutting them off at the potato. Some may have already begun to form roots if located along the bottom portion of the sweet potato. Just tease them out of the soil, trying not to break of any roots that are formed.
- Remove the lower leaves from the sprouts and place in a jar or glass of water to allow roots to form.
- To speed up the process you can place the jar on a heating mat or under a grow light. Roots should start forming in a couple of days.
- Change out the water once a week and remove any sprouts that have died and are not forming roots.
- Once the sprout has roots that are about 2-3 inches long you are ready to plant your slips.
- One whole sweet potato can yield about a dozen or more sprouts. You may have more slips than you can handle in your garden. Give them away to friends, family or to a school or community garden.
Caring for Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or compost, around the plants to retain soil moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds.
- Fertilization: Sweet potatoes generally do not require heavy fertilization. However, a balanced fertilizer applied at planting can promote healthy growth. Avoid high-nitrogen fertilizers, as they can lead to excessive vine growth at the expense of tuber development.
- Watering: Provide regular watering, especially during dry spells. Sweet potatoes need consistent moisture to develop properly, but overwatering can lead to rot. Aim for about 1 inch of water per week, adjusting based on rainfall and soil conditions.
Pest and Disease Management:
- Common Pests: Sweet potatoes can be affected by pests such as sweet potato weevils, wireworms, and aphids. Monitor the plants regularly and use appropriate organic or chemical controls if necessary. Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can help manage aphid populations.
- Disease Prevention: Sweet potatoes are susceptible to diseases like root rot and leaf spot. To minimize disease risk, practice crop rotation and avoid planting sweet potatoes in the same spot each year. Ensure good air circulation by spacing plants appropriately and removing any diseased foliage promptly.
Tips for Successful Growing:
- Black Plastic Mulch: For northern states, using black plastic mulch can help warm the soil and promote faster growth. Lay the plastic over the planting area and cut holes for planting the slips. This technique can be especially beneficial in cooler climates.
- Companion Planting: Plant sweet potatoes alongside companion plants like beans, marigolds, and nasturtiums to help repel pests and improve soil health.
- Crop Rotation: Rotate sweet potato crops with legumes or other non-related crops to reduce the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test before planting to determine nutrient levels and pH. Amend the soil as needed based on the test results to create optimal growing conditions.
- Avoiding Soil Compaction: Sweet potatoes need loose, well-aerated soil to develop properly. Avoid walking on the planting beds and consider raised beds if soil compaction is a concern.
- Weed Control: Keep the planting area weed-free, especially during the early stages of growth. Weeds can compete with sweet potatoes for nutrients and water, affecting overall yield.
Harvesting Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Timing: Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes are typically ready to harvest 90 to 105 days after planting. The vines will begin to yellow and die back, indicating that the tubers are mature.
- Harvesting: Use a garden fork or spade to carefully lift the sweet potatoes from the soil. Handle the tubers gently to avoid bruising or damaging the skin. Any cuts or bruises can lead to rot during storage.
- Curing: After harvesting, cure the sweet potatoes by placing them in a warm, humid environment (about 85°F with 85-90% humidity) for 7 to 10 days. Curing helps to heal any cuts and enhances the sweetness of the tubers.
- Storage: Once cured, store the sweet potatoes in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Ideal storage conditions are around 55°F with moderate humidity. Properly cured and stored sweet potatoes can last for several months.
Container Growing:
- While Red Japanese Sweet Potatoes are typically grown in the ground, they can also be grown in large containers. Choose a container that is at least 12 inches deep and has adequate drainage.
- Use a high-quality potting mix and ensure the container is placed in a sunny location. Follow the same care guidelines as for in-ground planting, paying special attention to watering needs as container plants can dry out more quickly.
By following these guidelines for growing and caring for Red Japanese Sweet Potato slips, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious sweet potatoes. With proper attention to their needs, these versatile and flavorful tubers will reward you with a delightful addition to your home garden. Happy gardening!
Here is a helpful article on how to grow sweet potatoes.
Includes 12 slips per pound. For delivery only; no store pick-up options available. All sales final.


Check Your Zone Compatibility:
Compatible with your zone.
Growing Zone for

Our Guarantee To You
Since 1976, we've served our customers at every stage of growing. Please contact us at any time. We are happy to support and assist you.
Shipping Information
Shipping Information
Shipping Weight: 1.1 lb
Features
Features
Characteristics
Characteristics
Planting & Care
Planting & Care
Useful Information
Useful Information
Guarantee
Guarantee
Share